Platensimycin Redux
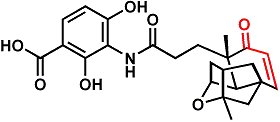
Last Saturday, the Journal of the American Chemical Society published the isolation and structure determination of the natural product antibiotic platensimycin.
The paper can be found here.
I posted about this compound at this link. The new paper demonstrates that the potentially reactive alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone (enone, highlighted in red in figure) does not appear to contribute to platensimycin's chemical mechanism of action, but the conformation of the ring containing the enone does seem to play a role.
Platensimycin adsorbs well to the drying agent magnesium sulfate, perhaps a little too well, because it was impossible to recover product from it. The ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid chelates the magnesium. No problem with sodium sulfate, though. You called it, Jack.
Labels: literature


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home